parse
编译过程首先就是对模板做解析,生成 AST,它是一种抽象语法树,是对源代码的抽象语法结构的树状表现形式。在很多编译技术中,如 babel 编译 ES6 的代码都会先生成 AST。
这个过程是比较复杂的,它会用到大量正则表达式对字符串解析,如果对正则不是很了解,建议先去补习正则表达式的知识。为了直观地演示 parse 的过程,我们先来看一个例子:
<ul :class="bindCls" class="list" v-if="isShow">
<li v-for="(item,index) in data" @click="clickItem(index)">
{{item}}:{{index}}
</li>
</ul>经过 parse 过程后,生成的 AST 如下:
ast = {
'type': 1,
'tag': 'ul',
'attrsList': [],
'attrsMap': {
':class': 'bindCls',
'class': 'list',
'v-if': 'isShow'
},
'if': 'isShow',
'ifConditions': [{
'exp': 'isShow',
'block': // ul ast element
}],
'parent': undefined,
'plain': false,
'staticClass': 'list',
'classBinding': 'bindCls',
'children': [{
'type': 1,
'tag': 'li',
'attrsList': [{
'name': '@click',
'value': 'clickItem(index)'
}],
'attrsMap': {
'@click': 'clickItem(index)',
'v-for': '(item,index) in data'
},
'parent': // ul ast element
'plain': false,
'events': {
'click': {
'value': 'clickItem(index)'
}
},
'hasBindings': true,
'for': 'data',
'alias': 'item',
'iterator1': 'index',
'children': [
'type': 2,
'expression': '_s(item)+":"+_s(index)'
'text': '{{item}}:{{index}}',
'tokens': [
{'@binding':'item'},
':',
{'@binding':'index'}
]
]
}]
}可以看到,生成的 AST 是一个树状结构,每一个节点都是一个 ast element,除了它自身的一些属性,还维护了它的父子关系,如 parent 指向它的父节点,children 指向它的所有子节点。先对 AST 有一些直观的印象,那么接下来我们来分析一下这个 AST 是如何得到的。
整体流程
首先来看一下 parse 的定义,在 src/compiler/parser/index.js 中:
export function parse(
template: string,
options: CompilerOptions
): ASTElement | void {
getFnsAndConfigFromOptions(options);
parseHTML(template, {
// options ...
start(tag, attrs, unary) {
let element = createASTElement(tag, attrs);
processElement(element);
treeManagement();
},
end() {
treeManagement();
closeElement();
},
chars(text: string) {
handleText();
createChildrenASTOfText();
},
comment(text: string) {
createChildrenASTOfComment();
},
});
return astRootElement;
}parse 函数的代码很长,贴一遍对同学的理解没有好处,我先把它拆成伪代码的形式,方便同学们对整体流程先有一个大致的了解。接下来我们就来分解分析每段伪代码的作用。
从 options 中获取方法和配置
对应伪代码:
getFnsAndConfigFromOptions(options);parse 函数的输入是 template 和 options,输出是 AST 的根节点。template 就是我们的模板字符串,而 options 实际上是和平台相关的一些配置,它的定义在 src/platforms/web/compiler/options 中:
import {
isPreTag,
mustUseProp,
isReservedTag,
getTagNamespace,
} from "../util/index";
import modules from "./modules/index";
import directives from "./directives/index";
import { genStaticKeys } from "shared/util";
import { isUnaryTag, canBeLeftOpenTag } from "./util";
export const baseOptions: CompilerOptions = {
expectHTML: true,
modules,
directives,
isPreTag,
isUnaryTag,
mustUseProp,
canBeLeftOpenTag,
isReservedTag,
getTagNamespace,
staticKeys: genStaticKeys(modules),
};这些属性和方法之所以放到 platforms 目录下是因为它们在不同的平台(web 和 weex)的实现是不同的。
我们用伪代码 getFnsAndConfigFromOptions 表示了这一过程,它的实际代码如下:
warn = options.warn || baseWarn;
platformIsPreTag = options.isPreTag || no;
platformMustUseProp = options.mustUseProp || no;
platformGetTagNamespace = options.getTagNamespace || no;
transforms = pluckModuleFunction(options.modules, "transformNode");
preTransforms = pluckModuleFunction(options.modules, "preTransformNode");
postTransforms = pluckModuleFunction(options.modules, "postTransformNode");
delimiters = options.delimiters;这些方法和配置都是后续解析时候需要的,可以不用去管它们的具体作用,我们先往后看。
解析 HTML 模板
对应伪代码:
parseHTML(template, options);对于 template 模板的解析主要是通过 parseHTML 函数,它的定义在 src/compiler/parser/html-parser 中:
export function parseHTML(html, options) {
let lastTag;
while (html) {
if (!lastTag || !isPlainTextElement(lastTag)) {
let textEnd = html.indexOf("<");
if (textEnd === 0) {
if (matchComment) {
advance(commentLength);
continue;
}
if (matchDoctype) {
advance(doctypeLength);
continue;
}
if (matchEndTag) {
advance(endTagLength);
parseEndTag();
continue;
}
if (matchStartTag) {
parseStartTag();
handleStartTag();
continue;
}
}
handleText();
advance(textLength);
} else {
handlePlainTextElement();
parseEndTag();
}
}
}由于 parseHTML 的逻辑也非常复杂,因此我也用了伪代码的方式表达,整体来说它的逻辑就是循环解析 template ,用正则做各种匹配,对于不同情况分别进行不同的处理,直到整个 template 被解析完毕。 在匹配的过程中会利用 advance 函数不断前进整个模板字符串,直到字符串末尾。
function advance(n) {
index += n;
html = html.substring(n);
}为了更加直观地说明 advance 的作用,可以通过一副图表示:
 调用
调用 advance 函数:
advance(4);得到结果: 
匹配的过程中主要利用了正则表达式,如下:
const attribute =
/^\s*([^\s"'<>\/=]+)(?:\s*(=)\s*(?:"([^"]*)"+|'([^']*)'+|([^\s"'=<>`]+)))?/;
const ncname = "[a-zA-Z_][\\w\\-\\.]*";
const qnameCapture = `((?:${ncname}\\:)?${ncname})`;
const startTagOpen = new RegExp(`^<${qnameCapture}`);
const startTagClose = /^\s*(\/?)>/;
const endTag = new RegExp(`^<\\/${qnameCapture}[^>]*>`);
const doctype = /^<!DOCTYPE [^>]+>/i;
const comment = /^<!\--/;
const conditionalComment = /^<!\[/;通过这些正则表达式,我们可以匹配注释节点、文档类型节点、开始闭合标签等。
- 注释节点、文档类型节点
对于注释节点和文档类型节点的匹配,如果匹配到我们仅仅做的是做前进即可。
if (comment.test(html)) {
const commentEnd = html.indexOf('-->')
if (commentEnd >= 0) {
if (options.shouldKeepComment) {
options.comment(html.substring(4, commentEnd))
}
advance(commentEnd + 3)
continue
}
}
if (conditionalComment.test(html)) {
const conditionalEnd = html.indexOf(']>')
if (conditionalEnd >= 0) {
advance(conditionalEnd + 2)
continue
}
}
const doctypeMatch = html.match(doctype)
if (doctypeMatch) {
advance(doctypeMatch[0].length)
continue
}对于注释和条件注释节点,前进至它们的末尾位置;对于文档类型节点,则前进它自身长度的距离。
- 开始标签
const startTagMatch = parseStartTag()
if (startTagMatch) {
handleStartTag(startTagMatch)
if (shouldIgnoreFirstNewline(lastTag, html)) {
advance(1)
}
continue
}首先通过 parseStartTag 解析开始标签:
function parseStartTag() {
const start = html.match(startTagOpen);
if (start) {
const match = {
tagName: start[1],
attrs: [],
start: index,
};
advance(start[0].length);
let end, attr;
while (
!(end = html.match(startTagClose)) &&
(attr = html.match(attribute))
) {
advance(attr[0].length);
match.attrs.push(attr);
}
if (end) {
match.unarySlash = end[1];
advance(end[0].length);
match.end = index;
return match;
}
}
}对于开始标签,除了标签名之外,还有一些标签相关的属性。函数先通过正则表达式 startTagOpen 匹配到开始标签,然后定义了 match 对象,接着循环去匹配开始标签中的属性并添加到 match.attrs 中,直到匹配的开始标签的闭合符结束。如果匹配到闭合符,则获取一元斜线符,前进到闭合符尾,并把当前索引赋值给 match.end。
parseStartTag 对开始标签解析拿到 match 后,紧接着会执行 handleStartTag 对 match 做处理:
function handleStartTag(match) {
const tagName = match.tagName;
const unarySlash = match.unarySlash;
if (expectHTML) {
if (lastTag === "p" && isNonPhrasingTag(tagName)) {
parseEndTag(lastTag);
}
if (canBeLeftOpenTag(tagName) && lastTag === tagName) {
parseEndTag(tagName);
}
}
const unary = isUnaryTag(tagName) || !!unarySlash;
const l = match.attrs.length;
const attrs = new Array(l);
for (let i = 0; i < l; i++) {
const args = match.attrs[i];
if (IS_REGEX_CAPTURING_BROKEN && args[0].indexOf('""') === -1) {
if (args[3] === "") {
delete args[3];
}
if (args[4] === "") {
delete args[4];
}
if (args[5] === "") {
delete args[5];
}
}
const value = args[3] || args[4] || args[5] || "";
const shouldDecodeNewlines =
tagName === "a" && args[1] === "href"
? options.shouldDecodeNewlinesForHref
: options.shouldDecodeNewlines;
attrs[i] = {
name: args[1],
value: decodeAttr(value, shouldDecodeNewlines),
};
}
if (!unary) {
stack.push({
tag: tagName,
lowerCasedTag: tagName.toLowerCase(),
attrs: attrs,
});
lastTag = tagName;
}
if (options.start) {
options.start(tagName, attrs, unary, match.start, match.end);
}
}handleStartTag 的核心逻辑很简单,先判断开始标签是否是一元标签,类似 <img>、<br/> 这样,接着对 match.attrs 遍历并做了一些处理,最后判断如果非一元标签,则往 stack 里 push 一个对象,并且把 tagName 赋值给 lastTag。至于 stack 的作用,稍后我会介绍。
最后调用了 options.start 回调函数,并传入一些参数,这个回调函数的作用稍后我会详细介绍。
- 闭合标签
const endTagMatch = html.match(endTag)
if (endTagMatch) {
const curIndex = index
advance(endTagMatch[0].length)
parseEndTag(endTagMatch[1], curIndex, index)
continue
}先通过正则 endTag 匹配到闭合标签,然后前进到闭合标签末尾,然后执行 parseEndTag 方法对闭合标签做解析。
function parseEndTag(tagName, start, end) {
let pos, lowerCasedTagName;
if (start == null) start = index;
if (end == null) end = index;
if (tagName) {
lowerCasedTagName = tagName.toLowerCase();
}
if (tagName) {
for (pos = stack.length - 1; pos >= 0; pos--) {
if (stack[pos].lowerCasedTag === lowerCasedTagName) {
break;
}
}
} else {
pos = 0;
}
if (pos >= 0) {
for (let i = stack.length - 1; i >= pos; i--) {
if (
process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production" &&
(i > pos || !tagName) &&
options.warn
) {
options.warn(`tag <${stack[i].tag}> has no matching end tag.`);
}
if (options.end) {
options.end(stack[i].tag, start, end);
}
}
stack.length = pos;
lastTag = pos && stack[pos - 1].tag;
} else if (lowerCasedTagName === "br") {
if (options.start) {
options.start(tagName, [], true, start, end);
}
} else if (lowerCasedTagName === "p") {
if (options.start) {
options.start(tagName, [], false, start, end);
}
if (options.end) {
options.end(tagName, start, end);
}
}
}parseEndTag 的核心逻辑很简单,在介绍之前我们回顾一下在执行 handleStartTag 的时候,对于非一元标签(有 endTag)我们都把它构造成一个对象压入到 stack 中,如图所示:
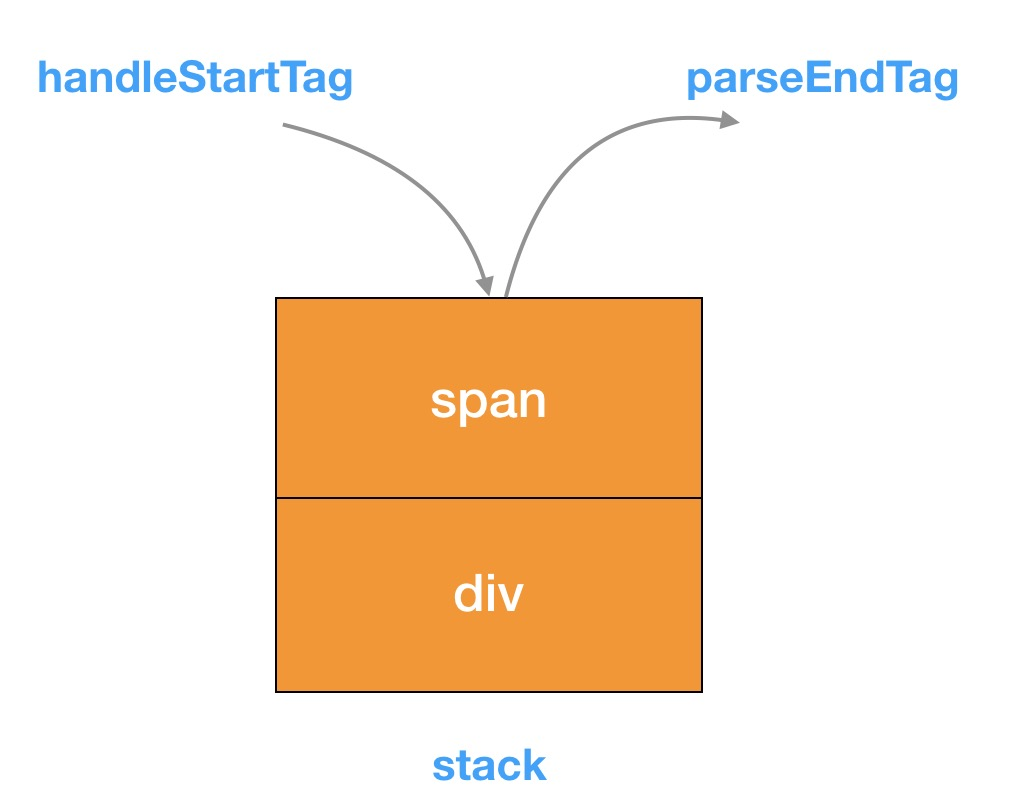
那么对于闭合标签的解析,就是倒序 stack,找到第一个和当前 endTag 匹配的元素。如果是正常的标签匹配,那么 stack 的最后一个元素应该和当前的 endTag 匹配,但是考虑到如下错误情况:
<div><span></div>这个时候当 endTag 为 </div> 的时候,从 stack 尾部找到的标签是 <span>,就不能匹配,因此这种情况会报警告。匹配后把栈到 pos 位置的都弹出,并从 stack 尾部拿到 lastTag。
最后调用了 options.end 回调函数,并传入一些参数,这个回调函数的作用稍后我会详细介绍。
- 文本
let text, rest, next;
if (textEnd >= 0) {
rest = html.slice(textEnd);
while (
!endTag.test(rest) &&
!startTagOpen.test(rest) &&
!comment.test(rest) &&
!conditionalComment.test(rest)
) {
next = rest.indexOf("<", 1);
if (next < 0) break;
textEnd += next;
rest = html.slice(textEnd);
}
text = html.substring(0, textEnd);
advance(textEnd);
}
if (textEnd < 0) {
text = html;
html = "";
}
if (options.chars && text) {
options.chars(text);
}接下来判断 textEnd 是否大于等于 0 的,满足则说明到从当前位置到 textEnd 位置都是文本,并且如果 < 是纯文本中的字符,就继续找到真正的文本结束的位置,然后前进到结束的位置。
再继续判断 textEnd 小于 0 的情况,则说明整个 template 解析完毕了,把剩余的 html 都赋值给了 text。
最后调用了 options.chars 回调函数,并传 text 参数,这个回调函数的作用稍后我会详细介绍。
因此,在循环解析整个 template 的过程中,会根据不同的情况,去执行不同的回调函数,下面我们来看看这些回调函数的作用。
处理开始标签
对应伪代码:
start (tag, attrs, unary) {
let element = createASTElement(tag, attrs)
processElement(element)
treeManagement()
}当解析到开始标签的时候,最后会执行 start 回调函数,函数主要就做 3 件事情,创建 AST 元素,处理 AST 元素,AST 树管理。下面我们来分别来看这几个过程。
- 创建 AST 元素
// check namespace.
// inherit parent ns if there is one
const ns = (currentParent && currentParent.ns) || platformGetTagNamespace(tag);
// handle IE svg bug
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (isIE && ns === "svg") {
attrs = guardIESVGBug(attrs);
}
let element: ASTElement = createASTElement(tag, attrs, currentParent);
if (ns) {
element.ns = ns;
}
export function createASTElement(
tag: string,
attrs: Array<Attr>,
parent: ASTElement | void
): ASTElement {
return {
type: 1,
tag,
attrsList: attrs,
attrsMap: makeAttrsMap(attrs),
parent,
children: [],
};
}通过 createASTElement 方法去创建一个 AST 元素,并添加了 namespace。可以看到,每一个 AST 元素就是一个普通的 JavaScript 对象,其中,type 表示 AST 元素类型,tag 表示标签名,attrsList 表示属性列表,attrsMap 表示属性映射表,parent 表示父的 AST 元素,children 表示子 AST 元素集合。
- 处理 AST 元素
if (isForbiddenTag(element) && !isServerRendering()) {
element.forbidden = true;
process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production" &&
warn(
"Templates should only be responsible for mapping the state to the " +
"UI. Avoid placing tags with side-effects in your templates, such as " +
`<${tag}>` +
", as they will not be parsed."
);
}
// apply pre-transforms
for (let i = 0; i < preTransforms.length; i++) {
element = preTransforms[i](element, options) || element;
}
if (!inVPre) {
processPre(element);
if (element.pre) {
inVPre = true;
}
}
if (platformIsPreTag(element.tag)) {
inPre = true;
}
if (inVPre) {
processRawAttrs(element);
} else if (!element.processed) {
// structural directives
processFor(element);
processIf(element);
processOnce(element);
// element-scope stuff
processElement(element, options);
}首先是对模块 preTransforms 的调用,其实所有模块的 preTransforms、 transforms 和 postTransforms 的定义都在 src/platforms/web/compiler/modules 目录中,这部分我们暂时不会介绍,之后会结合具体的例子说。接着判断 element 是否包含各种指令通过 processXXX 做相应的处理,处理的结果就是扩展 AST 元素的属性。这里我并不会一一介绍所有的指令处理,而是结合我们当前的例子,我们来看一下 processFor 和 processIf:
export function processFor(el: ASTElement) {
let exp;
if ((exp = getAndRemoveAttr(el, "v-for"))) {
const res = parseFor(exp);
if (res) {
extend(el, res);
} else if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production") {
warn(`Invalid v-for expression: ${exp}`);
}
}
}
export const forAliasRE = /(.*?)\s+(?:in|of)\s+(.*)/;
export const forIteratorRE = /,([^,\}\]]*)(?:,([^,\}\]]*))?$/;
const stripParensRE = /^\(|\)$/g;
export function parseFor(exp: string): ?ForParseResult {
const inMatch = exp.match(forAliasRE);
if (!inMatch) return;
const res = {};
res.for = inMatch[2].trim();
const alias = inMatch[1].trim().replace(stripParensRE, "");
const iteratorMatch = alias.match(forIteratorRE);
if (iteratorMatch) {
res.alias = alias.replace(forIteratorRE, "");
res.iterator1 = iteratorMatch[1].trim();
if (iteratorMatch[2]) {
res.iterator2 = iteratorMatch[2].trim();
}
} else {
res.alias = alias;
}
return res;
}processFor 就是从元素中拿到 v-for 指令的内容,然后分别解析出 for、alias、iterator1、iterator2 等属性的值添加到 AST 的元素上。就我们的示例 v-for="(item,index) in data" 而言,解析出的的 for 是 data,alias 是 item,iterator1 是 index,没有 iterator2。
function processIf(el) {
const exp = getAndRemoveAttr(el, "v-if");
if (exp) {
el.if = exp;
addIfCondition(el, {
exp: exp,
block: el,
});
} else {
if (getAndRemoveAttr(el, "v-else") != null) {
el.else = true;
}
const elseif = getAndRemoveAttr(el, "v-else-if");
if (elseif) {
el.elseif = elseif;
}
}
}
export function addIfCondition(el: ASTElement, condition: ASTIfCondition) {
if (!el.ifConditions) {
el.ifConditions = [];
}
el.ifConditions.push(condition);
}processIf 就是从元素中拿 v-if 指令的内容,如果拿到则给 AST 元素添加 if 属性和 ifConditions 属性;否则尝试拿 v-else 指令及 v-else-if 指令的内容,如果拿到则给 AST 元素分别添加 else 和 elseif 属性。
- AST 树管理
我们在处理开始标签的时候为每一个标签创建了一个 AST 元素,在不断解析模板创建 AST 元素的时候,我们也要为它们建立父子关系,就像 DOM 元素的父子关系那样。
AST 树管理相关代码如下:
function checkRootConstraints(el) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production") {
if (el.tag === "slot" || el.tag === "template") {
warnOnce(
`Cannot use <${el.tag}> as component root element because it may ` +
"contain multiple nodes."
);
}
if (el.attrsMap.hasOwnProperty("v-for")) {
warnOnce(
"Cannot use v-for on stateful component root element because " +
"it renders multiple elements."
);
}
}
}
// tree management
if (!root) {
root = element;
checkRootConstraints(root);
} else if (!stack.length) {
// allow root elements with v-if, v-else-if and v-else
if (root.if && (element.elseif || element.else)) {
checkRootConstraints(element);
addIfCondition(root, {
exp: element.elseif,
block: element,
});
} else if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production") {
warnOnce(
`Component template should contain exactly one root element. ` +
`If you are using v-if on multiple elements, ` +
`use v-else-if to chain them instead.`
);
}
}
if (currentParent && !element.forbidden) {
if (element.elseif || element.else) {
processIfConditions(element, currentParent);
} else if (element.slotScope) {
// scoped slot
currentParent.plain = false;
const name = element.slotTarget || '"default"';
(currentParent.scopedSlots || (currentParent.scopedSlots = {}))[name] =
element;
} else {
currentParent.children.push(element);
element.parent = currentParent;
}
}
if (!unary) {
currentParent = element;
stack.push(element);
} else {
closeElement(element);
}AST 树管理的目标是构建一颗 AST 树,本质上它要维护 root 根节点和当前父节点 currentParent。为了保证元素可以正确闭合,这里也利用了 stack 栈的数据结构,和我们之前解析模板时用到的 stack 类似。
当我们在处理开始标签的时候,判断如果有 currentParent,会把当前 AST 元素 push 到 currentParent.chilldren 中,同时把 AST 元素的 parent 指向 currentParent。
接着就是更新 currentParent 和 stack ,判断当前如果不是一个一元标签,我们要把它生成的 AST 元素 push 到 stack 中,并且把当前的 AST 元素赋值给 currentParent。
stack 和 currentParent 除了在处理开始标签的时候会变化,在处理闭合标签的时候也会变化,因此整个 AST 树管理要结合闭合标签的处理逻辑看。
处理闭合标签
对应伪代码:
end () {
treeManagement()
closeElement()
}当解析到闭合标签的时候,最后会执行 end 回调函数:
// remove trailing whitespace
const element = stack[stack.length - 1];
const lastNode = element.children[element.children.length - 1];
if (lastNode && lastNode.type === 3 && lastNode.text === " " && !inPre) {
element.children.pop();
}
// pop stack
stack.length -= 1;
currentParent = stack[stack.length - 1];
closeElement(element);首先处理了尾部空格的情况,然后把 stack 的元素弹一个出栈,并把 stack 最后一个元素赋值给 currentParent,这样就保证了当遇到闭合标签的时候,可以正确地更新 stack 的长度以及 currentParent 的值,这样就维护了整个 AST 树。
最后执行了 closeElement(element):
function closeElement(element) {
// check pre state
if (element.pre) {
inVPre = false;
}
if (platformIsPreTag(element.tag)) {
inPre = false;
}
// apply post-transforms
for (let i = 0; i < postTransforms.length; i++) {
postTransforms[i](element, options);
}
}closeElement 逻辑很简单,就是更新一下 inVPre 和 inPre 的状态,以及执行 postTransforms 函数,这些我们暂时都不必了解。
处理文本内容
对应伪代码:
chars (text: string) {
handleText()
createChildrenASTOfText()
}除了处理开始标签和闭合标签,我们还会在解析模板的过程中去处理一些文本内容:
const children = currentParent.children;
text =
inPre || text.trim()
? isTextTag(currentParent)
? text
: decodeHTMLCached(text)
: // only preserve whitespace if its not right after a starting tag
preserveWhitespace && children.length
? " "
: "";
if (text) {
let res;
if (!inVPre && text !== " " && (res = parseText(text, delimiters))) {
children.push({
type: 2,
expression: res.expression,
tokens: res.tokens,
text,
});
} else if (
text !== " " ||
!children.length ||
children[children.length - 1].text !== " "
) {
children.push({
type: 3,
text,
});
}
}文本构造的 AST 元素有 2 种类型,一种是有表达式的,type 为 2,一种是纯文本,type 为 3。在我们的例子中,文本就是 :,是个表达式,通过执行 parseText(text, delimiters) 对文本解析,它的定义在 src/compiler/parser/text-parser.js 中:
const defaultTagRE = /\{\{((?:.|\n)+?)\}\}/g;
const regexEscapeRE = /[-.*+?^${}()|[\]\/\\]/g;
const buildRegex = cached((delimiters) => {
const open = delimiters[0].replace(regexEscapeRE, "\\$&");
const close = delimiters[1].replace(regexEscapeRE, "\\$&");
return new RegExp(open + "((?:.|\\n)+?)" + close, "g");
});
export function parseText(
text: string,
delimiters?: [string, string]
): TextParseResult | void {
const tagRE = delimiters ? buildRegex(delimiters) : defaultTagRE;
if (!tagRE.test(text)) {
return;
}
const tokens = [];
const rawTokens = [];
let lastIndex = (tagRE.lastIndex = 0);
let match, index, tokenValue;
while ((match = tagRE.exec(text))) {
index = match.index;
// push text token
if (index > lastIndex) {
rawTokens.push((tokenValue = text.slice(lastIndex, index)));
tokens.push(JSON.stringify(tokenValue));
}
// tag token
const exp = parseFilters(match[1].trim());
tokens.push(`_s(${exp})`);
rawTokens.push({ "@binding": exp });
lastIndex = index + match[0].length;
}
if (lastIndex < text.length) {
rawTokens.push((tokenValue = text.slice(lastIndex)));
tokens.push(JSON.stringify(tokenValue));
}
return {
expression: tokens.join("+"),
tokens: rawTokens,
};
}parseText 首先根据分隔符(默认是 )构造了文本匹配的正则表达式,然后再循环匹配文本,遇到普通文本就 push 到 rawTokens 和 tokens 中,如果是表达式就转换成 _s(${exp}) push 到 tokens 中,以及转换成 {@binding:exp} push 到 rawTokens 中。
对于我们的例子 :,tokens 就是 [_s(item),'":"',_s(index)];rawTokens 就是 [{'@binding':'item'},':',{'@binding':'index'}]。那么返回的对象如下:
return {
expression: '_s(item)+":"+_s(index)',
tokens: [{ "@binding": "item" }, ":", { "@binding": "index" }],
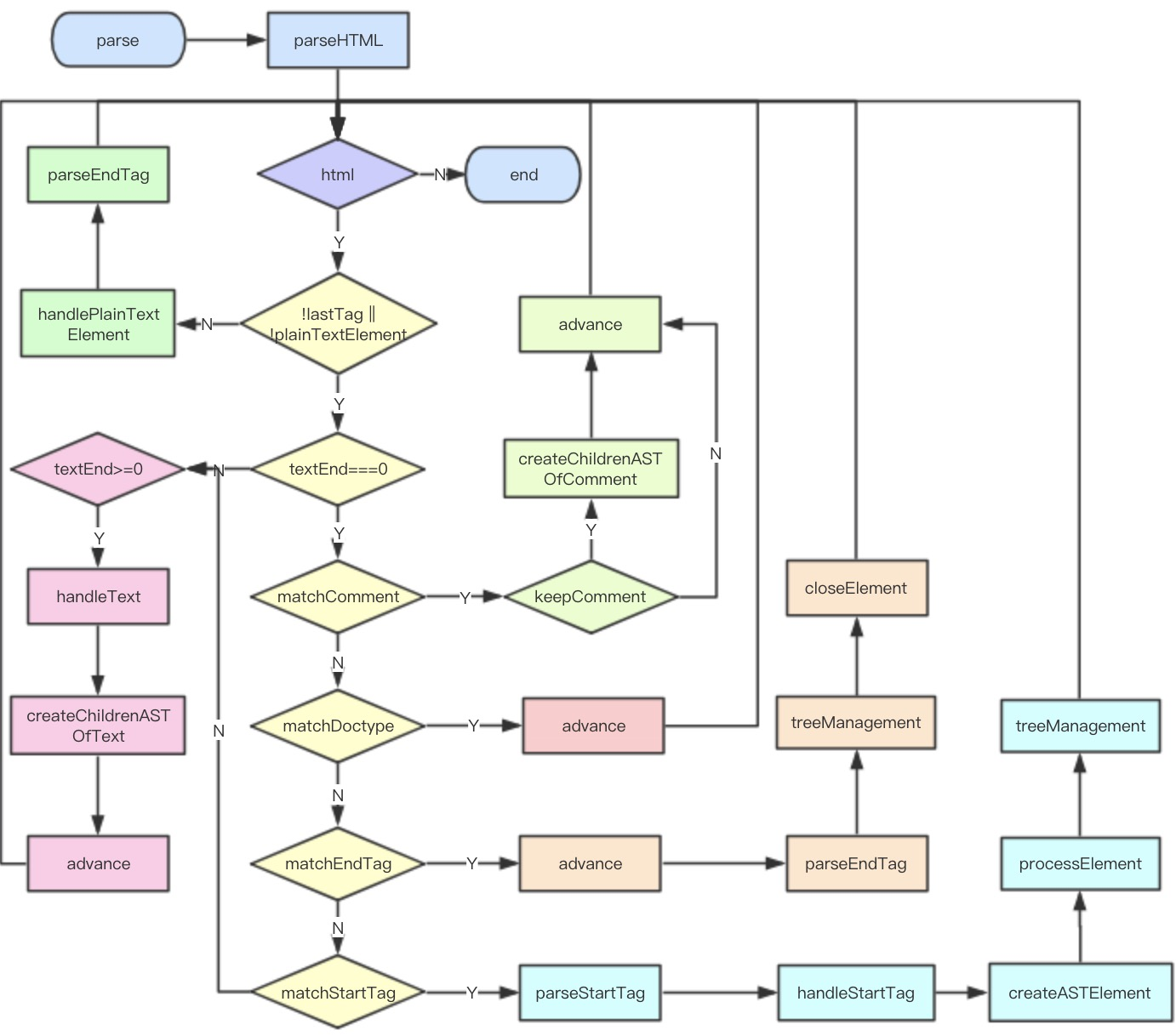
};流程图
总结
那么至此,parse 的过程就分析完了,看似复杂,但我们可以抛开细节理清它的整体流程。parse 的目标是把 template 模板字符串转换成 AST 树,它是一种用 JavaScript 对象的形式来描述整个模板。那么整个 parse 的过程是利用正则表达式顺序解析模板,当解析到开始标签、闭合标签、文本的时候都会分别执行对应的回调函数,来达到构造 AST 树的目的。
AST 元素节点总共有 3 种类型,type 为 1 表示是普通元素,为 2 表示是表达式,为 3 表示是纯文本。其实这里我觉得源码写的不够友好,这种是典型的魔术数字,如果转换成用常量表达会更利于源码阅读。
当 AST 树构造完毕,下一步就是 optimize 优化这颗树。